🌒 Waxing Crescent
🌓 First Quarter
🌔 Waxing Gibbous
🌕 Full
🌖 Waning Gibbous
🌗 Third Quarter
🌘 Waning Crescent

If you have looked into the night sky, you may have noticed the Moon appears to change shape each night. Some nights, the Moon might look like a narrow crescent. Other nights, the Moon might look like a bright circle. And on other nights, you might not be able to see the Moon at all. The different shapes of the Moon that we see at different times of the month are called the Moon’s phases.

The Moon’s appearance changes throughout the month. Credit: NASA's Scientific Visualization Studio
Why does this happen? The shape of the Moon isn’t changing throughout the month. However, our view of the Moon does change.
The Moon does not produce its own light. There is only one source of light in our solar system, and that is the Sun. Without the Sun, our Moon would be completely dark. What you may have heard referred to as “moonlight” is actually just sunlight reflecting off of the Moon’s surface.
The Sun’s light comes from one direction, and it always illuminates, or lights up, one half of the Moon – the side of the Moon that is facing the Sun. The other side of the Moon is dark.
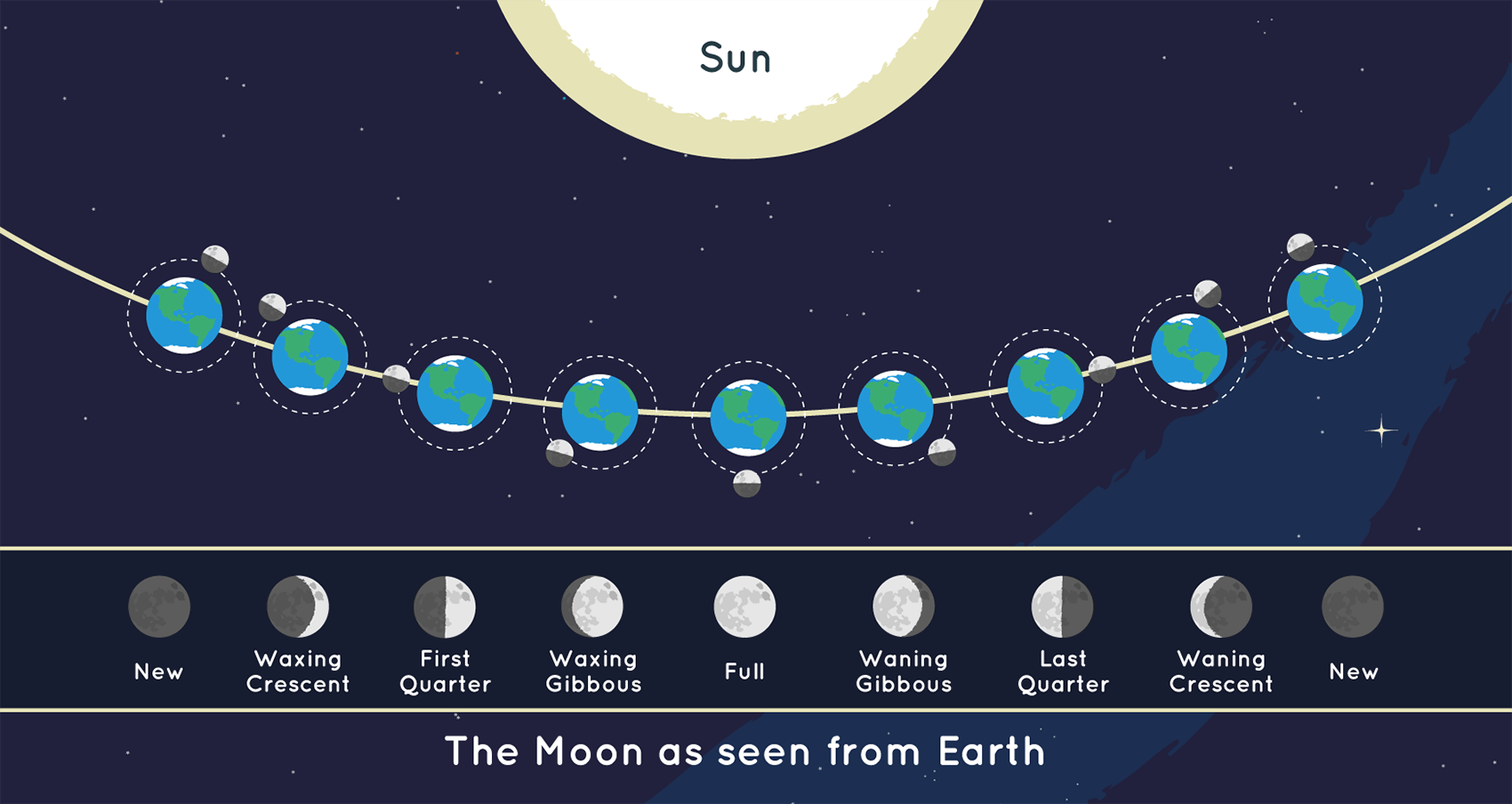
The position of the Moon and the Sun during Each of the Moon’s phases and the Moon as it appears from Earth during each phase. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
On Earth, our view of the illuminated part of the Moon changes each night, depending on where the Moon is in its orbit, or path, around Earth. When we have a full view of the completely illuminated side of the Moon, that phase is known as a full moon.
But following the night of each full moon, as the Moon orbits around Earth, we start to see less of the Moon lit by the Sun. Eventually, the Moon reaches a point in its orbit when we don’t see any of the Moon illuminated. At that point, the far side of the Moon is facing the Sun. This phase is called a new moon. During the new moon, the side facing Earth is dark.
The eight Moon phases:
🌑 New: We cannot see the Moon when it is a new moon.
🌒 Waxing Crescent: In the Northern Hemisphere, we see the waxing crescent phase as a thin crescent of light on the right.
🌓 First Quarter: We see the first quarter phase as a half moon.
🌔 Waxing Gibbous: The waxing gibbous phase is between a half moon and full moon. Waxing means it is getting bigger.
🌕 Full: We can see the Moon completely illuminated during full moons.
🌖 Waning Gibbous: The waning gibbous phase is between a full moon and a half moon. Waning means it is getting smaller.
🌗 Third Quarter: We see the third quarter moon as a half moon, too. It is the opposite half as illuminated in the first quarter moon.
🌘 Waning Crescent: In the Northern Hemisphere, we see the waning crescent phase as a thin crescent of light on the left.
The Moon displays these eight phases one after the other as it moves through its cycle each month. It takes about 27.3 days for the Moon to orbit Earth. However, because of how sunlight hits the Moon, it takes about 29.5 days to go from one new moon to the next new moon.
Here’s what the Moon looks like right now from Earth:
Use this tool to see the current Moon phase and to plan ahead for other Moon views. Credit: NASA
Interested in learning more about the Moon?
- Learn all about our Moon here.
- Learn about the types of full moons here.
- Learn why the Moon has craters here.
- Learn about lunar eclipses here.
- Make Oreo Moon phases!
Related Resources for Educators
Daily Moon Guide
Moon Phases Simulation Viewed from Earth and Space
Our World: Moon Phases
Make a Moon Phase Calendar and Calculator