What is an eclipse?
Below, check out a visualization of the April 8, 2024, total solar eclipse!
What’s the difference between a lunar eclipse and a solar eclipse?
Solar Eclipse
A solar eclipse happens when the Moon gets in the way of the Sun’s light and casts its shadow on Earth. That means during the day, the Moon moves over the Sun and it gets dark. Isn’t it strange that it gets dark in the middle of the day?
This total eclipse happens about every year and a half somewhere on Earth. A partial eclipse, when the Moon doesn’t completely cover the Sun, happens at least twice a year somewhere on Earth.
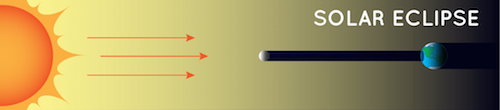
Note: This diagram is not to scale. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
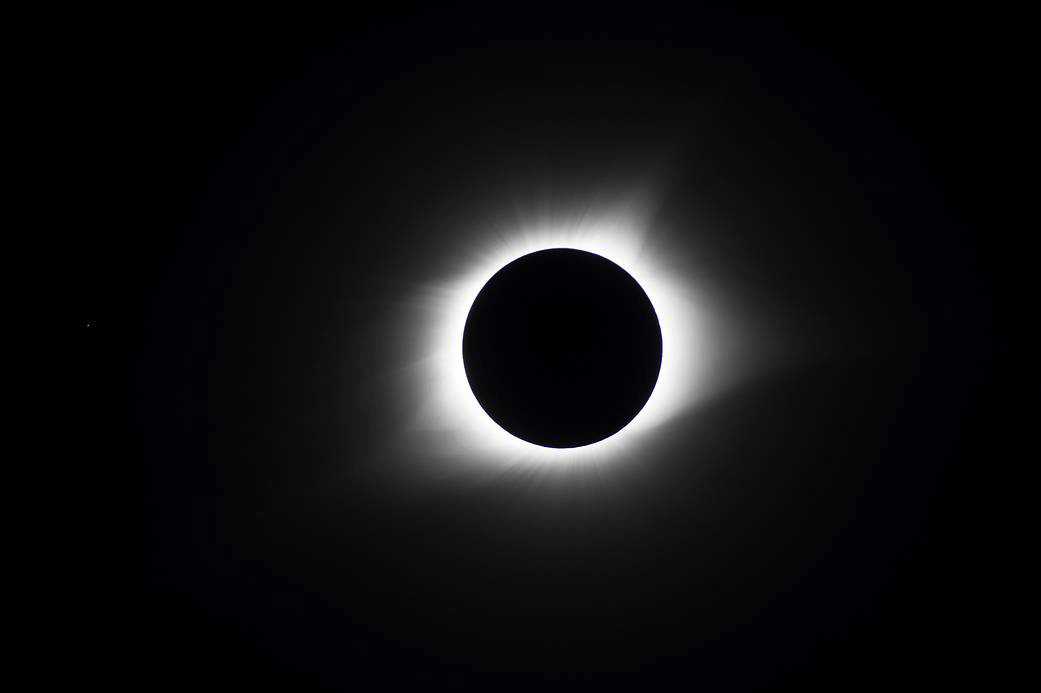

A total solar eclipse was visible over the continental United States on Aug. 21, 2017. This image was captured in Hopkinsville, Kentucky during the 2017 eclipse. Credit: NASA/MSFC/Joseph Matus
But not everyone experiences every solar eclipse. Getting a chance to see a total solar eclipse is rare. The Moon’s shadow on Earth isn’t very big, so only a small portion of places on Earth will see it. You have to be on the sunny side of the planet when it happens. You also have to be in the path of the Moon’s shadow.
On average, the same spot on Earth only gets to see a solar eclipse for a few minutes about every 375 years!
Caution!
Eye Safety During a Total Solar Eclipse
Except during the brief total phase of a total solar eclipse, when the Moon completely blocks the Sun’s bright face, it is not safe to look directly at the Sun without specialized eye protection for solar viewing.
For safety information, visit the NASA Eclipse Safety Page.
Lunar Eclipse
During a lunar eclipse, Earth gets in the way of the Sun’s light hitting the Moon. That means that during the night, a full moon fades away as Earth’s shadow covers it up.
The Moon can also look reddish because Earth’s atmosphere absorbs the other colors while it bends some sunlight toward the Moon. Sunlight bending through the atmosphere and absorbing other colors is also why sunsets are orange and red.
During a total lunar eclipse, the Moon is shining from all the sunrises and sunsets occurring on Earth!
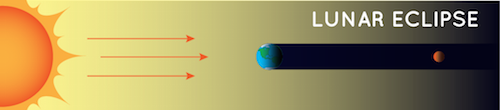
Note: This diagram is not to scale. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
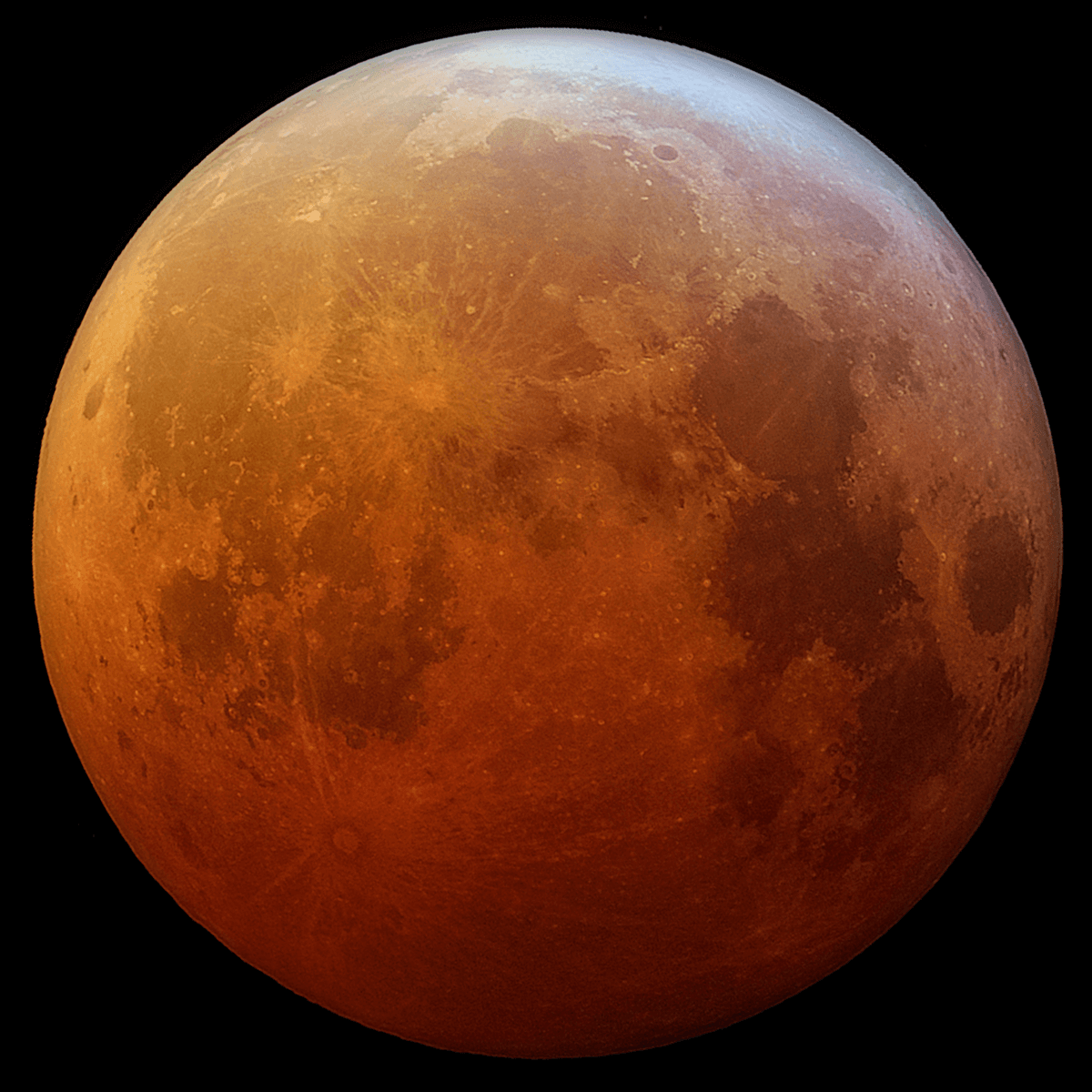
The Moon appeared a reddish color during a total lunar eclipse on Jan. 21, 2019 Credit: Public Domain
Why don’t we have a lunar eclipse every month?
You might be wondering why we don’t have a lunar eclipse every month as the Moon orbits Earth. It’s true that the Moon goes around Earth every month, but it doesn’t always get in Earth’s shadow. The Moon’s path around Earth is tilted compared to Earth’s orbit around the Sun. The Moon can be behind Earth but still get hit by light from the Sun.
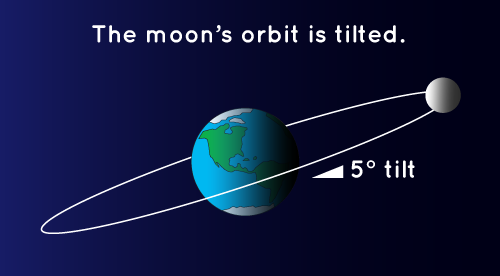
In this diagram, you can see that the Moon’s orbit around Earth is at a tilt. This is why we don’t get a lunar eclipse every month. This diagram is not to scale: the Moon is much farther away from Earth than shown here. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
Because they don’t happen every month, a lunar eclipse is a special event. Unlike solar eclipses, lots of people get to see each lunar eclipse. If you live on the nighttime half of Earth when the eclipse happens, you’ll be able to see it.
Remembering the Difference
It’s easy to get these two types of eclipses mixed up. An easy way to remember the difference is in the name. The name tells you what gets darker when the eclipse happens. In a solar eclipse, the Sun gets darker. In a lunar eclipse, the Moon gets darker.