Watch this video to learn all about nebulae! Click here to download this video (1920x1080, 334 MB, video/mp4).
A nebula is a giant cloud of dust and gas in space. Some nebulae (more than one nebula) come from the gas and dust thrown out by the explosion of a dying star, such as a supernova. Other nebulae are regions where new stars are beginning to form. For this reason, some nebulae are called "star nurseries."

These towers of cosmic dust and gas make up part of the Eagle Nebula. These so-called Pillars of Creation are part of an active star-forming region within the nebula. Credits: NASA, ESA and the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA)
How do stars form in a nebula?
Nebulae are made of dust and gases—mostly hydrogen and helium. The dust and gases in a nebula are very spread out, but gravity can slowly begin to pull together clumps of dust and gas. As these clumps get bigger and bigger, their gravity gets stronger and stronger.

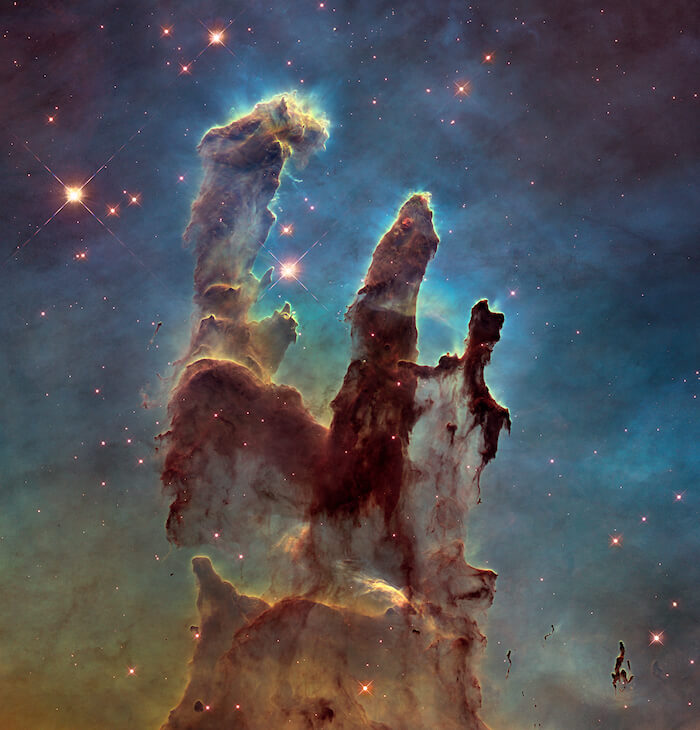
This landscape of "mountains" and "valleys" speckled with glittering stars is actually the edge of a nearby, young, star-forming region called NGC 3324 in the Carina Nebula. Captured in infrared light by NASA's James Webb Space Telescope, this image reveals for the first time previously invisible areas of star birth. Credits: NASA, ESA, CSA, and STScI
Eventually, the clump of dust and gas gets so big that it collapses from its own gravity. The collapse causes the material at the center of the cloud to heat up-and this hot core is the beginning of a star.
Where are nebulae?
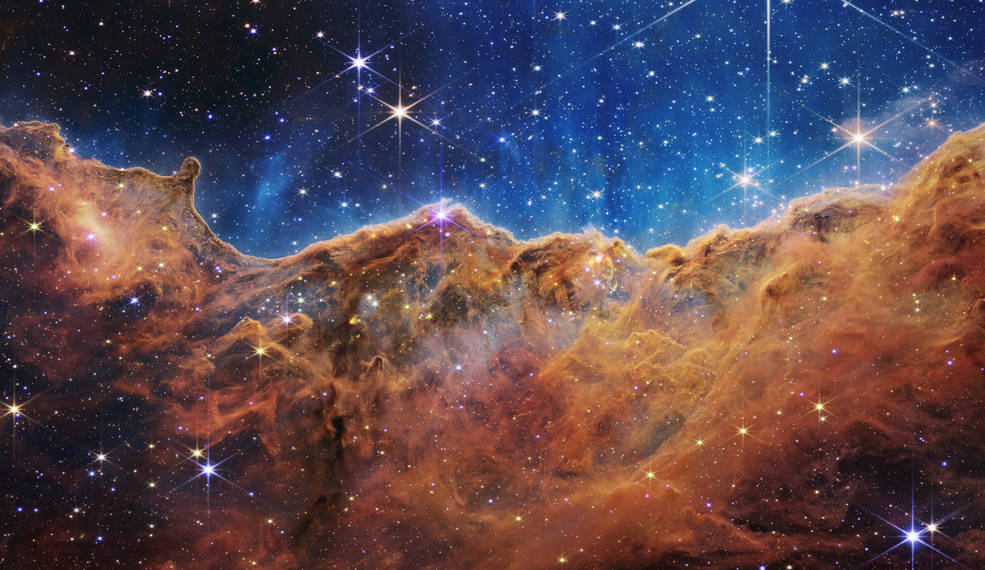
Nebulae exist in the space between the stars—also known as interstellar space. The closest known nebula to Earth is called the Helix Nebula. It is the remnant of a dying star—possibly one like the Sun. It is approximately 700 light-years away from Earth. That means even if you could travel at the speed of light, it would still take you 700 years to get there!

This image might look like a creepy eyeball, but it's actually a nebula! NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope captured this image of the Helix Nebula, which is located in the constellation Aquarius-about 700 light-years away from Earth. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Univ. of Arizona
How do we know what nebulae look like?
Astronomers use very powerful telescopes to take pictures of faraway nebulae. Space telescopes such as NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope and Hubble Space Telescope have captured many images of faraway nebulae.