The letters in the word laser stand for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation. A laser is an unusual light source. It is quite different from a light bulb or a flash light. Lasers produce a very narrow beam of light. This type of light is useful for lots of technologies and instruments—even some that you might use at home!
How does a laser work?
Light travels in waves, and the distance between the peaks of a wave is called the wavelength.
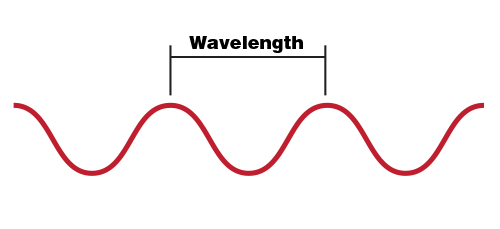
Each color of light has a different wavelength. For example, blue light has a shorter wavelength than red light. Sunlight—and the typical light from a lightbulb—is made up of light with many different wavelengths. Our eyes see this mixture of wavelengths as white light.
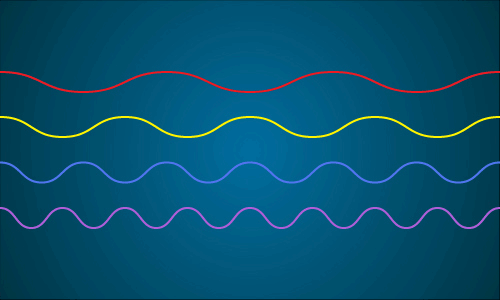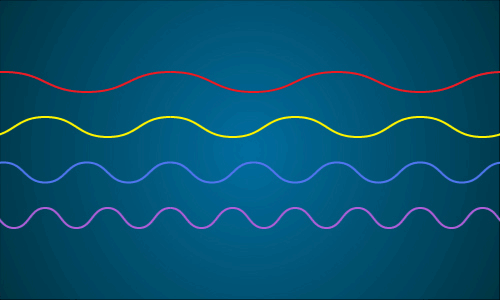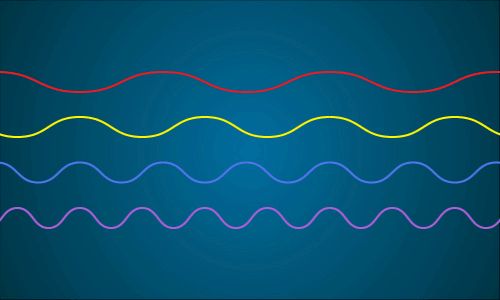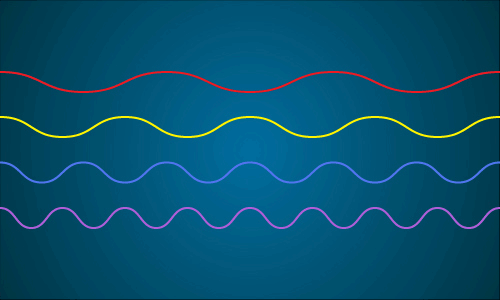
This animation shows a representation of the different wavelengths present in sunlight. When all of the different wavelengths (colors) come together, you get white light. Image credit: NASA
A laser is different. Lasers do not occur in nature. However, we have figured ways to artificially create this special type of light. Lasers produce a narrow beam of light in which all of the light waves have very similar wavelengths. The laser’s light waves travel together with their peaks all lined up, or in phase. This is why laser beams are very narrow, very bright, and can be focused into a very tiny spot.
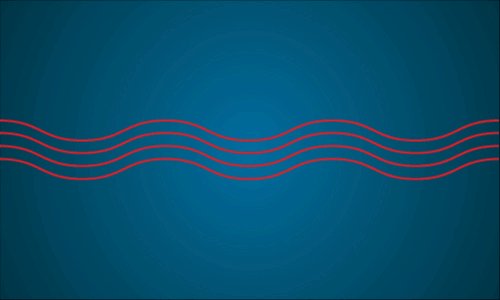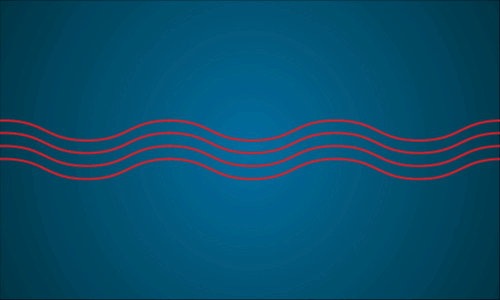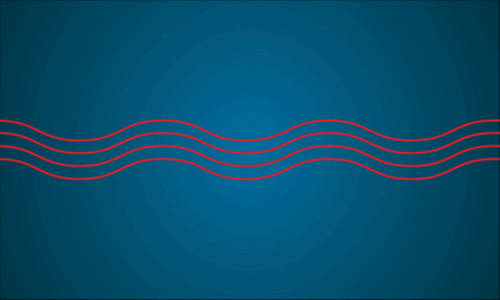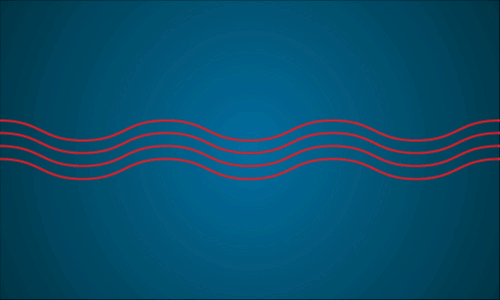
This animation is a representation of in phase laser light waves. Image credit: NASA
Because laser light stays focused and does not spread out much (like a flashlight would), laser beams can travel very long distances. They can also concentrate a lot of energy on a very small area.
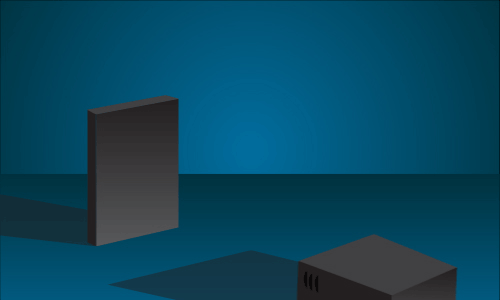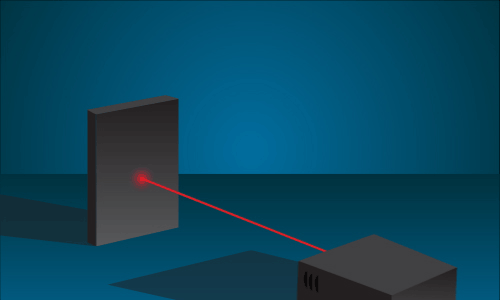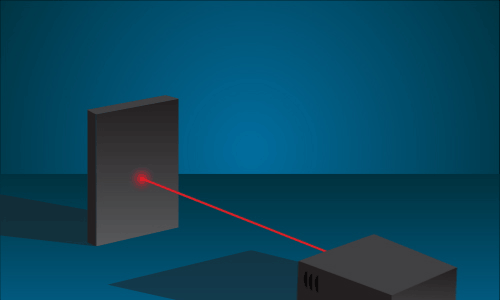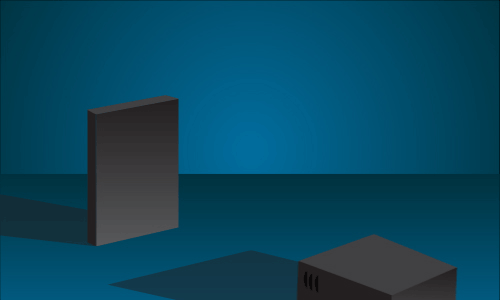
This animation shows how a laser can focus all of its light into one small point. Credit: NASA
Lasers have many uses. They are used in precision tools and can cut through diamonds or thick metal. They can also be designed to help in delicate surgeries. Lasers are used for recording and retrieving information. They are used in communications and in carrying TV and internet signals. We also find them in laser printers, bar code scanners, and DVD players. They also help to make parts for computers and other electronics.
Lasers are also used in instruments called spectrometers. Spectrometers can help scientists figure out what things are made of. For example, the Curiosity rover uses a laser spectrometer to see what kinds of chemicals are in certain rocks on Mars.

This is a picture of Martian soil before (left) and after (right) it was zapped by the Curiosity rover’s laser instrument called ChemCam. By zapping tiny holes in Martian soil and rock, ChemCam can determine what the material is made of. Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/LANL/ CNES/IRAP/LPGN/CNRS
NASA missions have used lasers to study the gases in Earth’s atmosphere. Lasers have also been used in instruments that map the surfaces of planets, moons, and asteroids.
Scientists have even measured the distance between the moon and Earth using lasers! By measuring the amount of time it takes for a laser beam to travel to the moon and back, astronomers can tell exactly how far away it is!